What are the 4 broad areas of need in SEND?
[vc_row type=”in_container” full_screen_row_position=”middle” scene_position=”center” text_color=”dark” text_align=”left” overlay_strength=”0.3″ shape_divider_position=”bottom”][vc_column column_padding=”no-extra-padding” column_padding_position=”all” background_color_opacity=”1″ background_hover_color_opacity=”1″ column_shadow=”none” column_border_radius=”none” width=”1/1″ tablet_text_alignment=”default” phone_text_alignment=”default” column_border_width=”none” column_border_style=”solid”][vc_column_text]
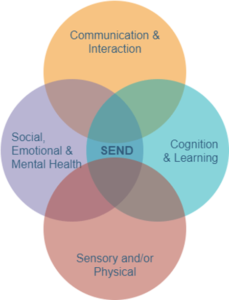
The four broad areas of need in SEND in education:
It’s extremely important to support all students in the education sector, including those with special education needs (SEN). Most children with special education needs attend mainstream schools, with 2019 statistics revealing 14.9% of overall pupils in the UK require SEN.
In this article, we aim to boost your knowledge about the four different areas of SEND (Special Education Needs and Disabilities) and how to effectively support those students.
There are four broad areas of SEND, which are:
- Communication and Interaction (C&I)
- Cognition and Learning (C&L)
- Social, Emotional and Mental Health Difficulties (SEMHD)
- Physical and/or Sensory Needs (P&SN)
Communication and Interaction:
The term often associated with Communication and Interaction is Speech, Language & Communication Needs (SLCN). There’s a large variety of issues linked to SLCN, which are;
- Issues producing sound
- Issues understanding language
- Issues using language
- Issues using and understanding non-verbal communication
- Pupils with Asperger’s syndrome and Autistic Spectrum Disorder (ASD) also fall into this category.
Cognition and Learning:
There’s a range of difficulties children face in this area:
Dyslexia – difficulty in learning to read or interpret words, letters, and other symbols
- Dyscalculia – severe difficulty in making math calculations, result of brain disorder
- Dyspraxia – condition affecting physical coordination
- Dysgraphia – neurological disorder that appears when children are learning to write
- Moderate Learning Difficulty (MLD)
- Severe Learning Difficulty (SLD)
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Social, Emotional and Mental Health Difficulties (SEMH):

This area of SEND focuses on the feelings of SEND students, for example if the student is;
- Withdrawn or isolating themselves
- Hyperactive or lack of concentration
- Immature in social situations
Certain disorders can be recognised under this area, such as Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD), Attention Deficit Hyperactive Disorder (ADHD), Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD), anxiety or attachment disorder.
Sensory and/or Physical Needs:

Students who have sensory or physical needs may have a:
- Physical disability
- Vision impairment
- Hearing impairment
- Multi-sensory impairment
- Dyspraxia
If a child’s additional needs are ignored, this can lead to future problems and behaviours that challenge authority. This could be seen with frequent disruptions, lack of progress and distracting other pupils.
So, you’re probably wondering how you can help a child who requires SEND? Here’s a few tips:
- A safe environment for the pupil
- Great communication between the child, their parents, therapists, teachers etc.
- Frequent and direct eye contact
- Praising the student; gold stars, stickers, target boards
- Creative ideas and innovative methods
- Not reacting to attention-seeking behaviour
- A clear and consistent routine
- Avoiding complicated instructions; short and sweet
- Giving the student enough time to respond
- Help build friendships; peer mentoring, buddies, friendship buddies
If you would like to keep up-to-date with Balfor Education, make sure to follow all of our social media pages! Find us on Instagram, Twitter, Facebook and LinkedIn, where we post frequent updates and announcements.
If you would like to apply for SEN teaching jobs in Birmingham, follow the link below:
https://balfor.co.uk/sen-teaching-jobs-birmingham/[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row type=”in_container” full_screen_row_position=”middle” scene_position=”center” text_color=”dark” text_align=”left” overlay_strength=”0.3″ shape_divider_position=”bottom”][vc_column column_padding=”no-extra-padding” column_padding_position=”all” background_color_opacity=”1″ background_hover_color_opacity=”1″ column_shadow=”none” column_border_radius=”none” width=”1/1″ tablet_text_alignment=”default” phone_text_alignment=”default” column_border_width=”none” column_border_style=”solid”][nectar_btn size=”large” open_new_tab=”true” button_style=”regular” button_color_2=”Accent-Color” icon_family=”none” url=”https://balfor.co.uk/jobs/” text=”Apply Now!”][/vc_column][/vc_row]
